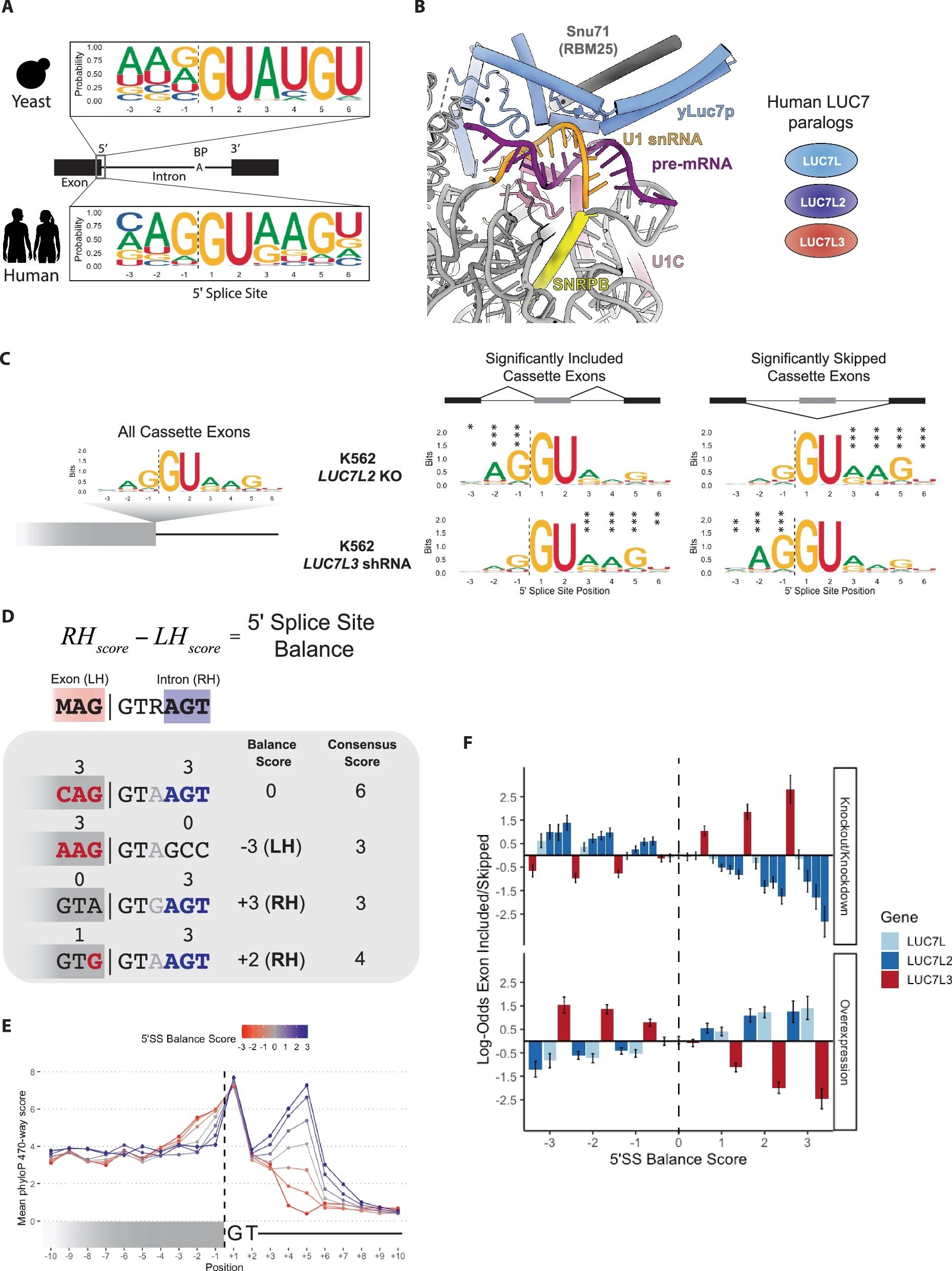
LUC7 proteins define two major classes of 5’ splice sites in animals and plants
Figure 1. Human LUC7 proteins impact 5′ splice sites with distinct composition. Kenny et al. Nature Communications 2025.

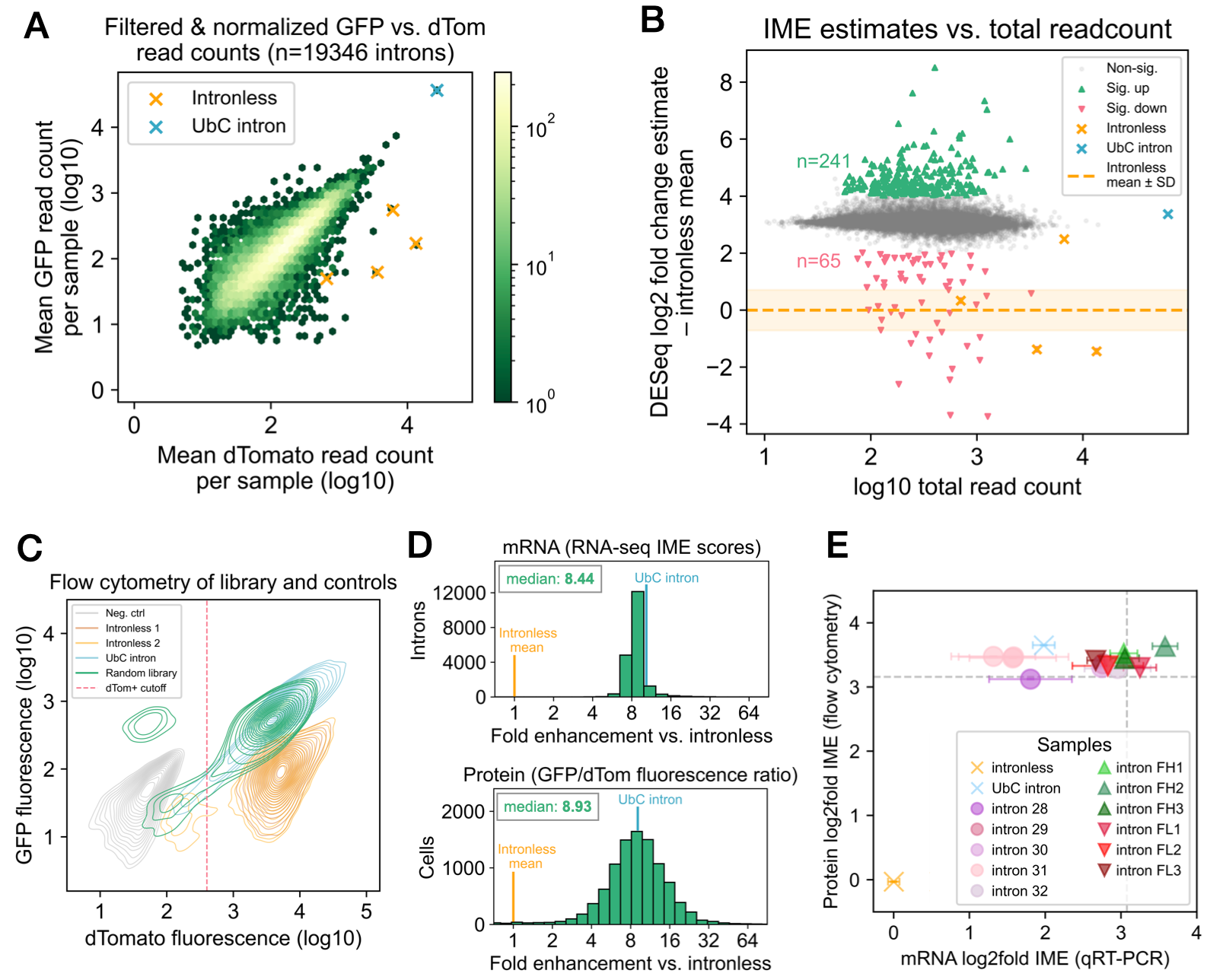
Sequence-dependent and -independent effects of intron-mediated enhancement learned from thousands of random introns
Figure 3. Almost all short random introns splice efficiently. Kowal et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025.

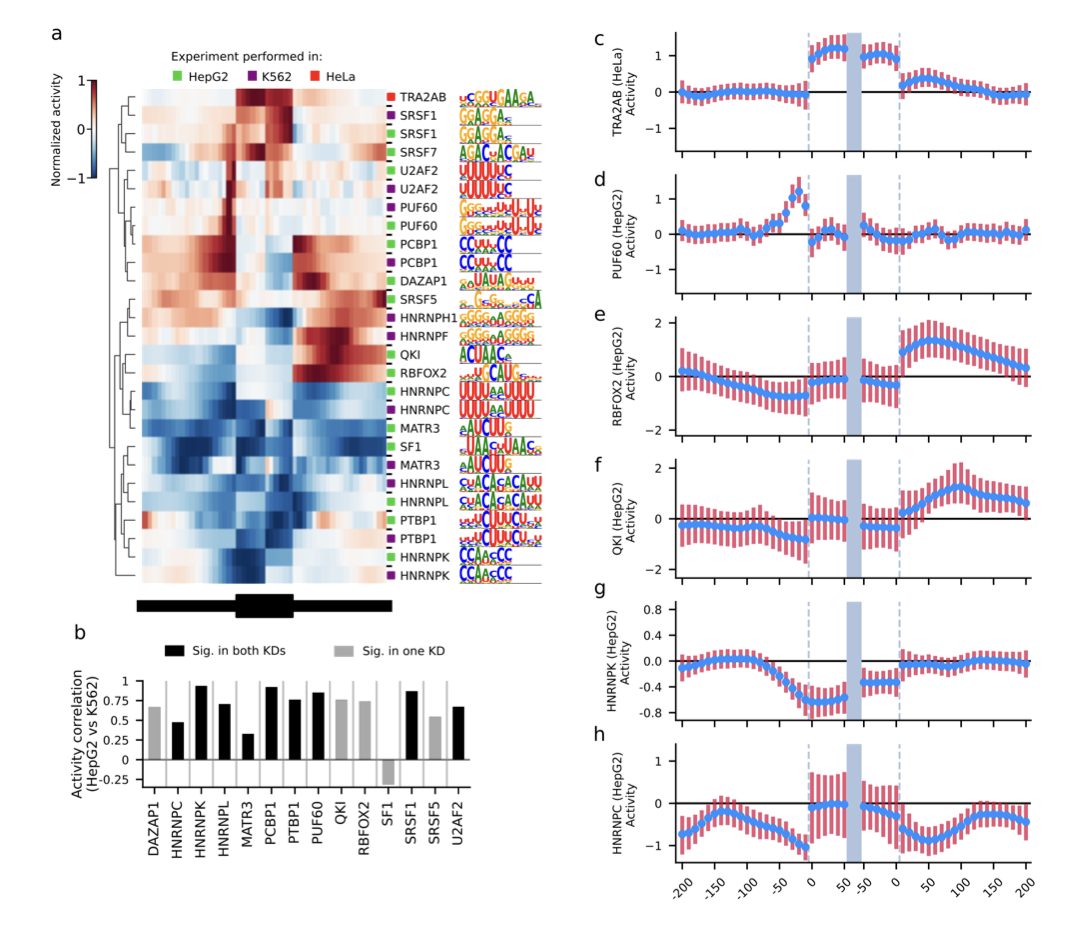
KATMAP: Inferring splicing factor activity and regulatory targets from knockdown data
Figure 2. KATMAP robustly infers splicing activity. McGurk et al. 2024 (Preprint).

PrevNext